The Ultimate Guide to Bio-Pharmaceutical Fittings
A comprehensive guide to BPE Fittings.
We’re going to break down every component of our most specialized style of fittings.
Are you new to the Bio-Pharmaceutical industry? This article is for you.


CHAPTER 01
Introducing Bio-Pharmaceutical Fittings

The Difference Between BPE Fittings and Standard (3A) Fittings

CHAPTER 03
BPE Surface Finishes

CHAPTER 04
Who Uses BPE Fittings and Why?

CHAPTER 05
Standards & Certification
Introducing Bio-Pharmaceutical Fittings
Sanitary fittings are used to manufacture a wide range of products for different industries including beverage, food, and pharmaceuticals.
All of these industries have guidelines and practices which must be adhered to with regards to cleanliness and production practices.
Of all the industries utilizing sanitary fittings for production methods, the pharmaceutical is the most demanding. There is no room for error in the production of medicines used to treat headaches up to and including the myriad of life-saving drugs consumed by the general public.
Given the need for strict production processes, the pharmaceutical industry cannot rely on standard sanitary fittings to manufacture drugs and other medicines. Enter BioPharmaceutical fittings or BPE fittings. This article will explain the differences between BPE fittings and standard sanitary fittings as well as detail some properties unique to this style of fittings.
The Difference Between BPE Fittings and Standard (3A) Fittings
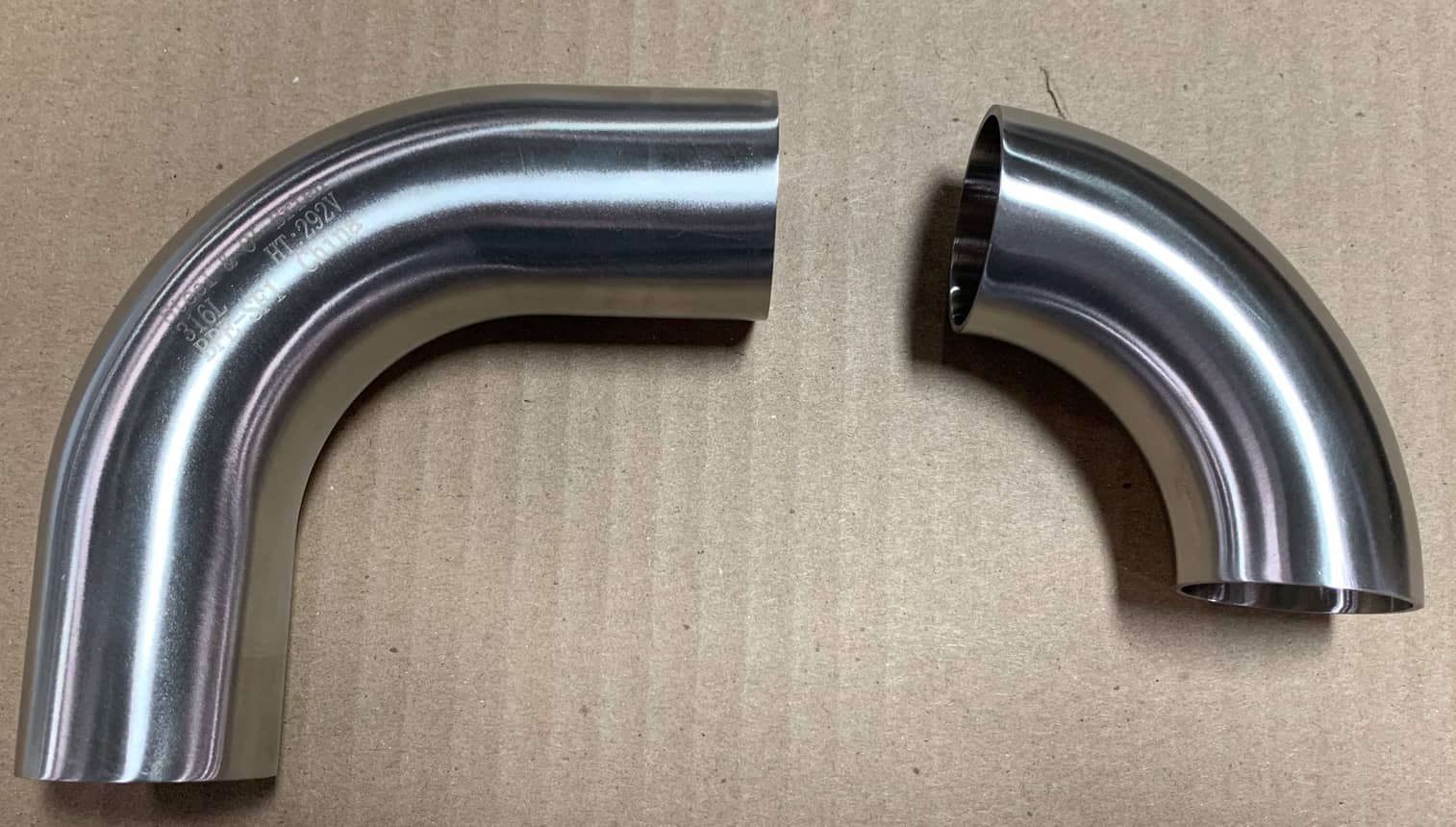
From a visual perspective, BPE Fittings may appear identical to 3A sanitary fittings. However, there are some important items such as tolerance and packaging that separate the two styles.
BioProcessing Equipment fittings, more commonly referred to as BPE, Bio-Pharm, or High-Purity fittings, comply with ASME-BPE standards. Given the critical nature of the products they are used to produce, BPE fittings are held to tighter tolerances and require a cleaner interior surface finish than standard fittings. The material requirements are also stricter than 3A Sanitary Standards for fittings typically used in food, beverage, and dairy processing applications.
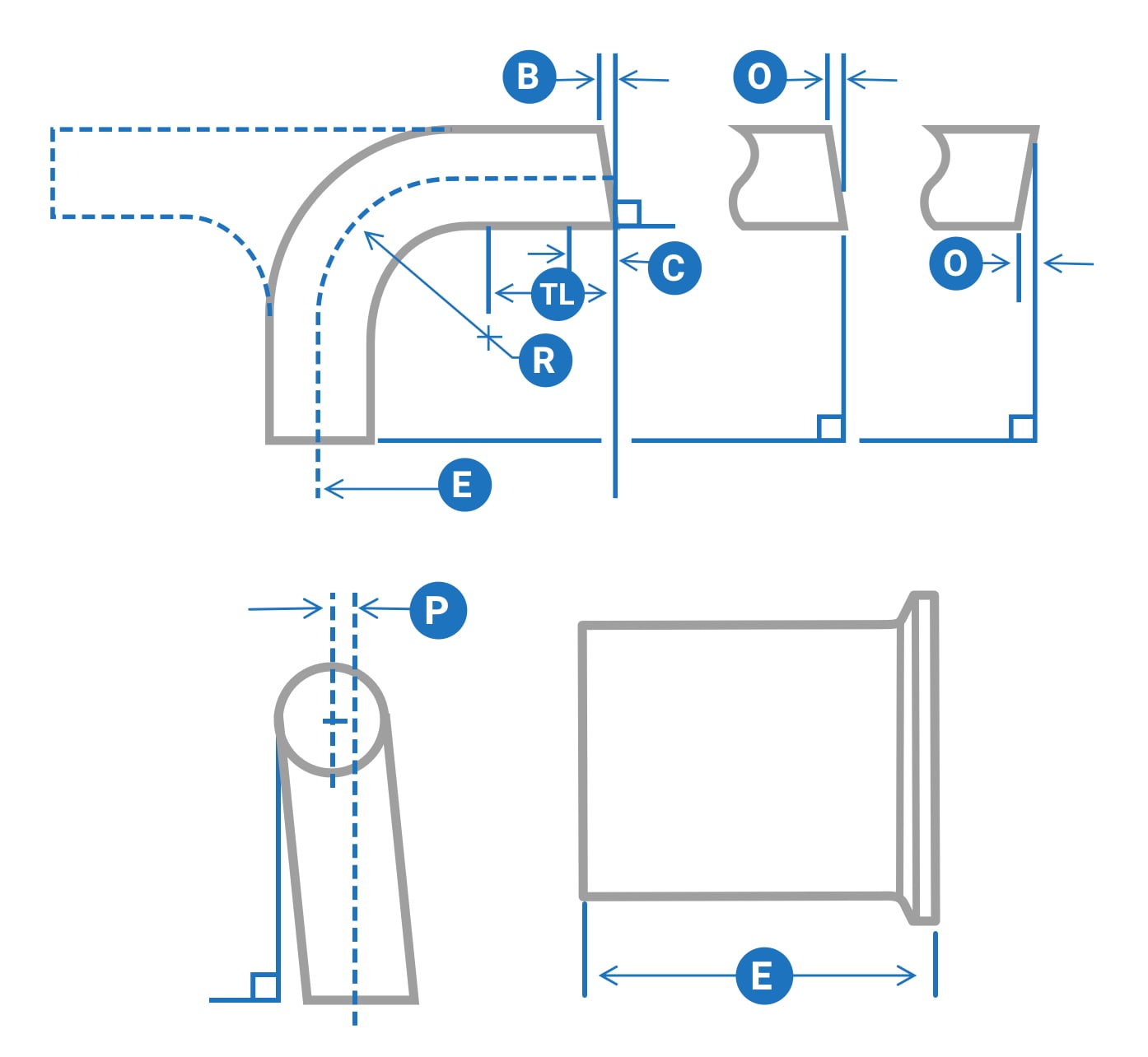
In order to comply with ASME-BPE Standards, all BPE fittings are dimensionally consistent regardless of manufacturer. Refer to the table of tolerances below for all BPE Fittings.
Table DT 3-1 Final Tolerances for Mechanically Polished Fittings and Process Components
Squareness to Face
Also defined as flatness, how flat is the face of the fitting
Control portion length
For BPE fittings this is generally .750 length, this area has specific tolerances
End-to-End, Center-to-End
Center-to-face or overall length dimension
Off Angle
This measures more of the overall fittings vs just the face. The flatness can be good however if the angle can be off. (92 deg elbow that is supposed to be 90)
Off Plane
Overall fitting tolerance to address any deformation
Tangent Length
Minimum tangent length on most weld ends
Centerline Radius of an elbow
Industry-standard is 1.5 x OD, not including 1/2″ size (example 1-1/2″ elbow has 2.250 R
| Nominal Size, in. | O.D. | Wall Thickness | Squareness Face to Tangent, B | Off Angle, 0 | Equivalent Angle (for 0) deg | Off Plane, P | Centerline Radius (CLR), R | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| in. | mm | in. | mm | in. | mm | in. | mm | in. | mm | in. | mm | ||
| ¼ | ±0.005 | ±0.13 | +0.003/-0.004 | +0.08/-0.10 | 0.005 | 0.13 | 0.009 | 0.23 | 2.1 | 0.030 | 0.76 | 0.563 | 14.30 |
| ⅜ | ±0.005 | ±0.13 | +0.003/-0.004 | +0.08/-0.10 | 0.005 | 0.13 | 0.012 | 0.30 | 1.8 | 0.030 | 0.76 | 1.125 | 28.58 |
| ½ | ±0.005 | ±0.13 | +0.005/-0.008 | +0.13/-0.20 | 0.005 | 0.13 | 0.014 | 0.36 | 1.6 | 0.030 | 0.76 | 1.125 | 28.58 |
| ¾ | ±0.005 | ±0.13 | +0.005/-0.008 | +0.13/-0.20 | 0.005 | 0.13 | 0.018 | 0.46 | 1.4 | 0.030 | 0.76 | 1.125 | 28.58 |
| 1 | ±0.005 | ±0.13 | +0.005/-0.008 | +0.13/-0.20 | 0.008 | 0.20 | 0.025 | 0.64 | 1.4 | 0.030 | 0.76 | 1.500 | 38.10 |
| 1½ | ±0.008 | ±0.20 | +0.005/-0.008 | +0.13/-0.20 | 0.008 | 0.20 | 0.034 | 0.86 | 1.3 | 0.050 | 1.27 | 2.250 | 57.15 |
| 2 | ±0.008 | ±0.20 | +0.005/-0.008 | +0.13/-0.20 | 0.008 | 0.20 | 0.043 | 1.09 | 1.2 | 0.050 | 1.27 | 3.000 | 76.20 |
| 2½ | ±0.010 | ±0.25 | +0.005/-0.008 | +0.13/-0.20 | 0.010 | 0.25 | 0.054 | 1.73 | 1.2 | 0.050 | 1.27 | 3.750 | 95.25 |
| 3 | ±0.010 | ±0.25 | +0.005/-0.008 | +0.13/-0.20 | 0.016 | 0.41 | 0.068 | 1.73 | 1.3 | 0.050 | 1.27 | 4.500 | 114.30 |
| 4 | ±0.015 | ±0.38 | +0.008/-0.010 | +0.20/-0.25 | 0.016 | 0.41 | 0.068 | 2.18 | 1.2 | 0.060 | 1.52 | 6.000 | 152.40 |
| 6 | ±0.030 | ±0.76 | +0.015/-0.015 | +0.38/-0.38 | 0.030 | 0.76 | 0.135 | 3.43 | 1.3 | 0.060 | 1.52 | 9.000 | 228.60 |
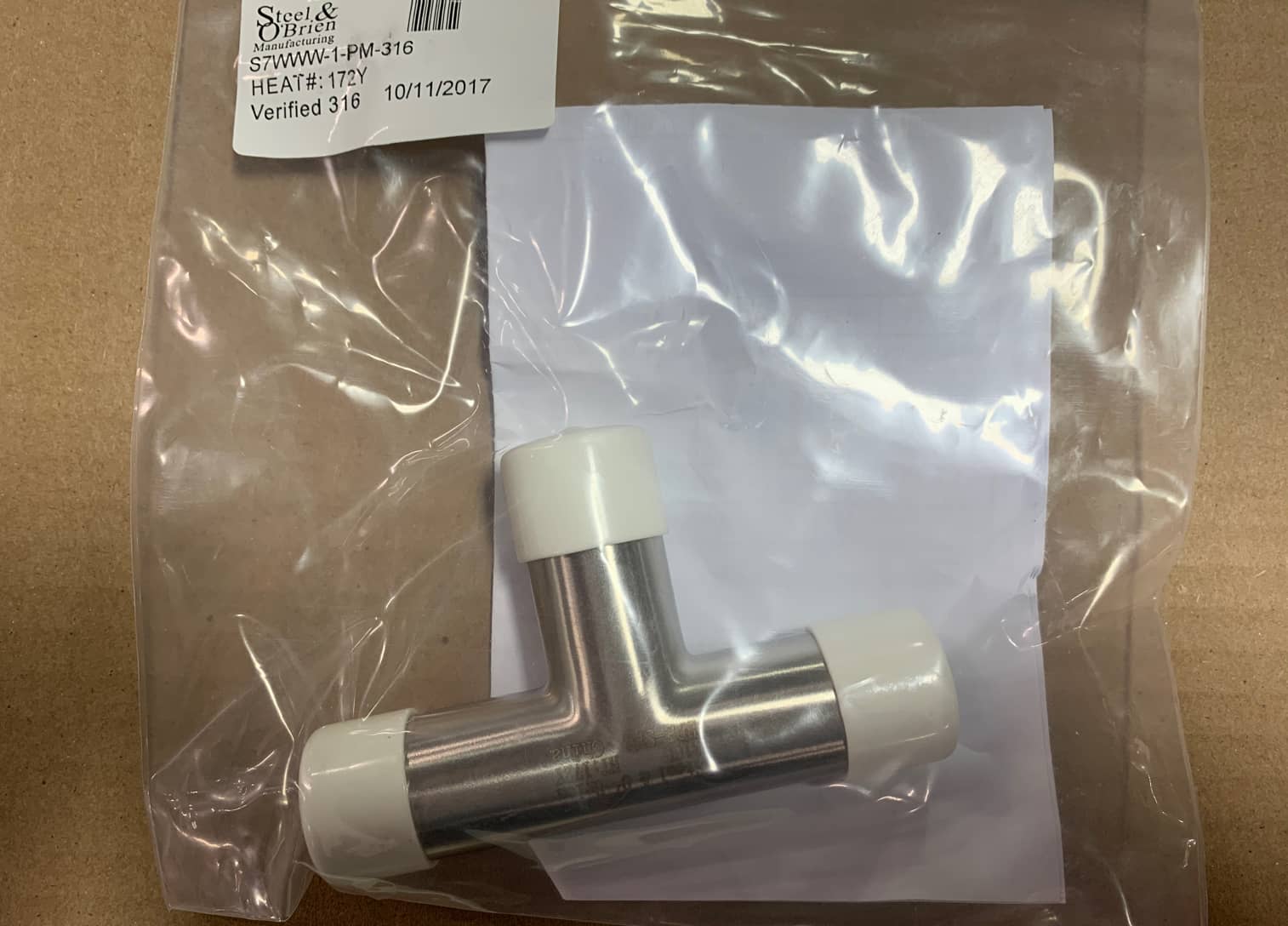
ASME-BPE fittings are required to have specific permanent marking on the outside of the fitting. This marking includes and is not limited to, heat number, material type, company, country of origin, surface finish and “BPE”.
Along with required markings, BPE fittings must be capped and bagged for shipment, as shown below.
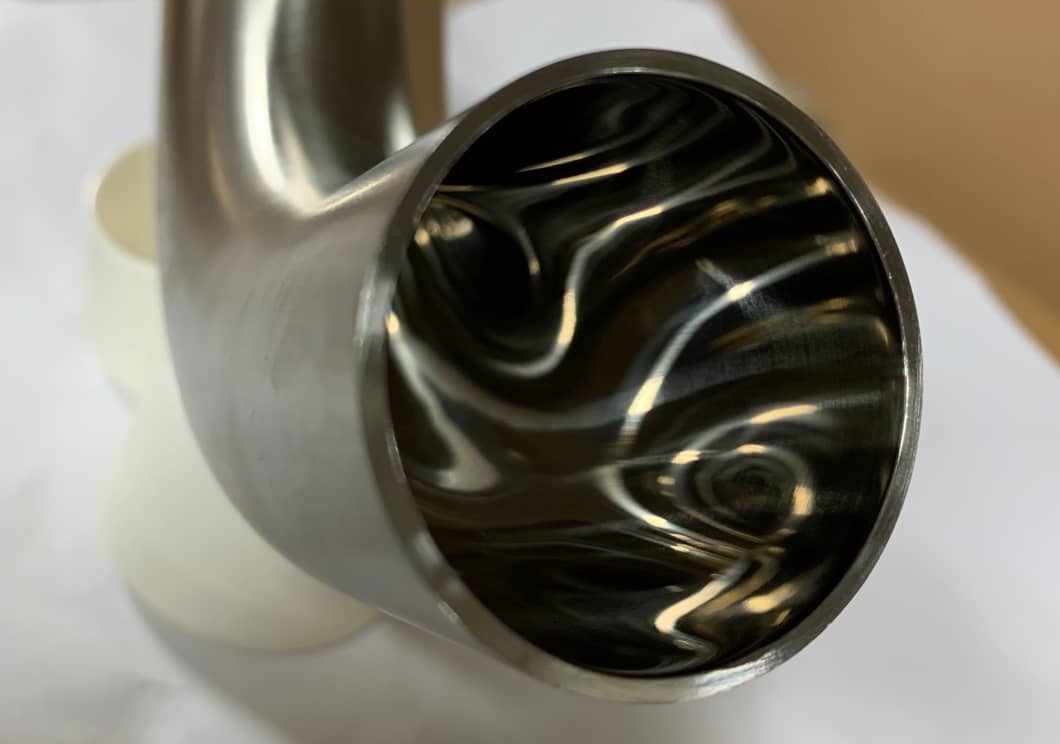
BPE Surface Finishes
Surface finish is a critical characteristic in the BPE spectrum given the importance of cleanliness within bioprocessing applications.
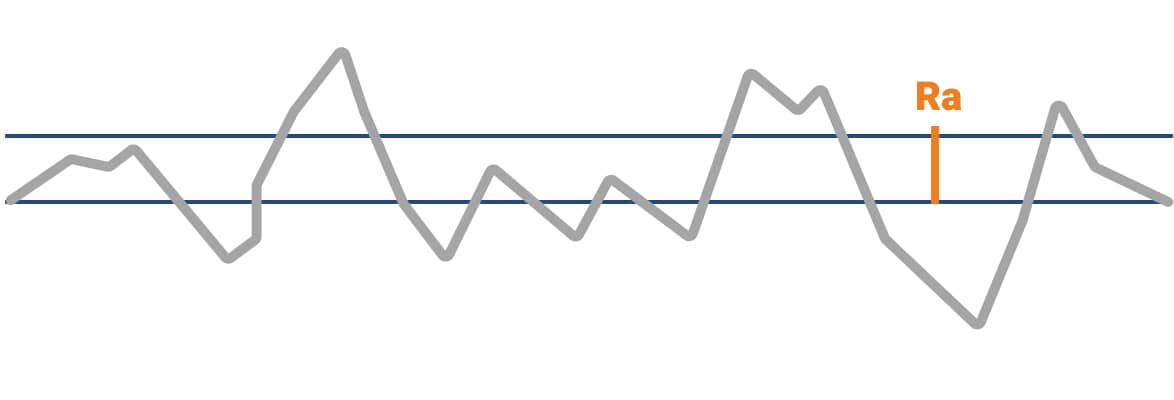
If you could look at stainless steel under a powerful microscope, you would see that even the smoothest steel is not as smooth as it would appear.
In fact, the steel would appear course and somewhat rough in nature. Roughness Average (Ra) refers to how smooth or rough the stainless steel is.
The roughness of the interior surface of the fittings is generally measured with a profilometer and measures roughness average (Ra), which is measured in microinches. Roughness average measures the peaks and valleys of the surface of the steel. The lower the Ra, the smoother the surface. BPE fittings are typically offered in two finishes: 20Ra, and a smoother, 15Ra with electropolish.
Cross section of a fitting at a microscopic level
It should be noted that the spec does not address the outside surface which should not come in contact with the product. By comparison, 3A fittings require an interior surface finish of at least 32Ra meaning they are less smooth than BPE fittings.
BPE Fitting with SF1, 20Ra Finish
BPE Fitting with SF4, 15Ra withFinish
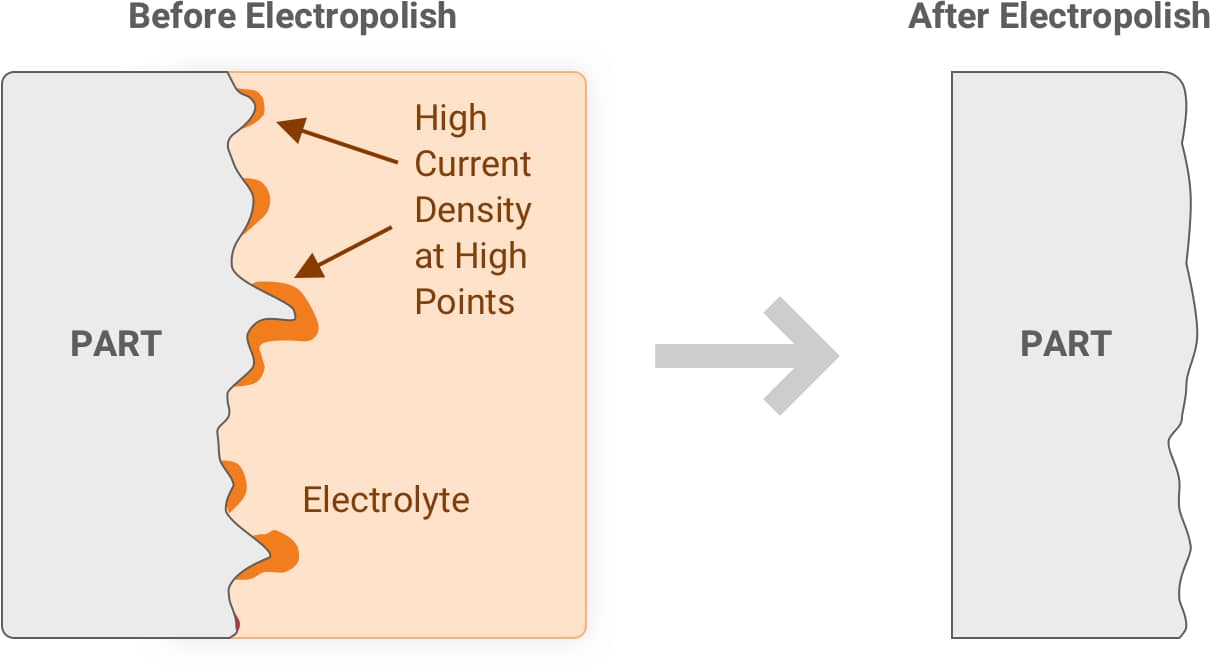
Electropolishing is an electrochemical process that removes material from the metal, thus lowering the difference between the peaks and valleys and creating an extremely smooth and mirror-like surface. During the electropolishing process, the part is immersed in an acid-based bath and subjected to direct electrical current. Actual metal is removed from the targeted surface to create the desired surface finish.
Magnified View
Who Uses BPE Fittings and Why?
BPE fittings are used by end-users and vendors supporting the biotechnology, pharmaceutical, and other high purity industries.
BPE fittings are used for their cleanliness, consistent dimensions, and consistent tolerances.
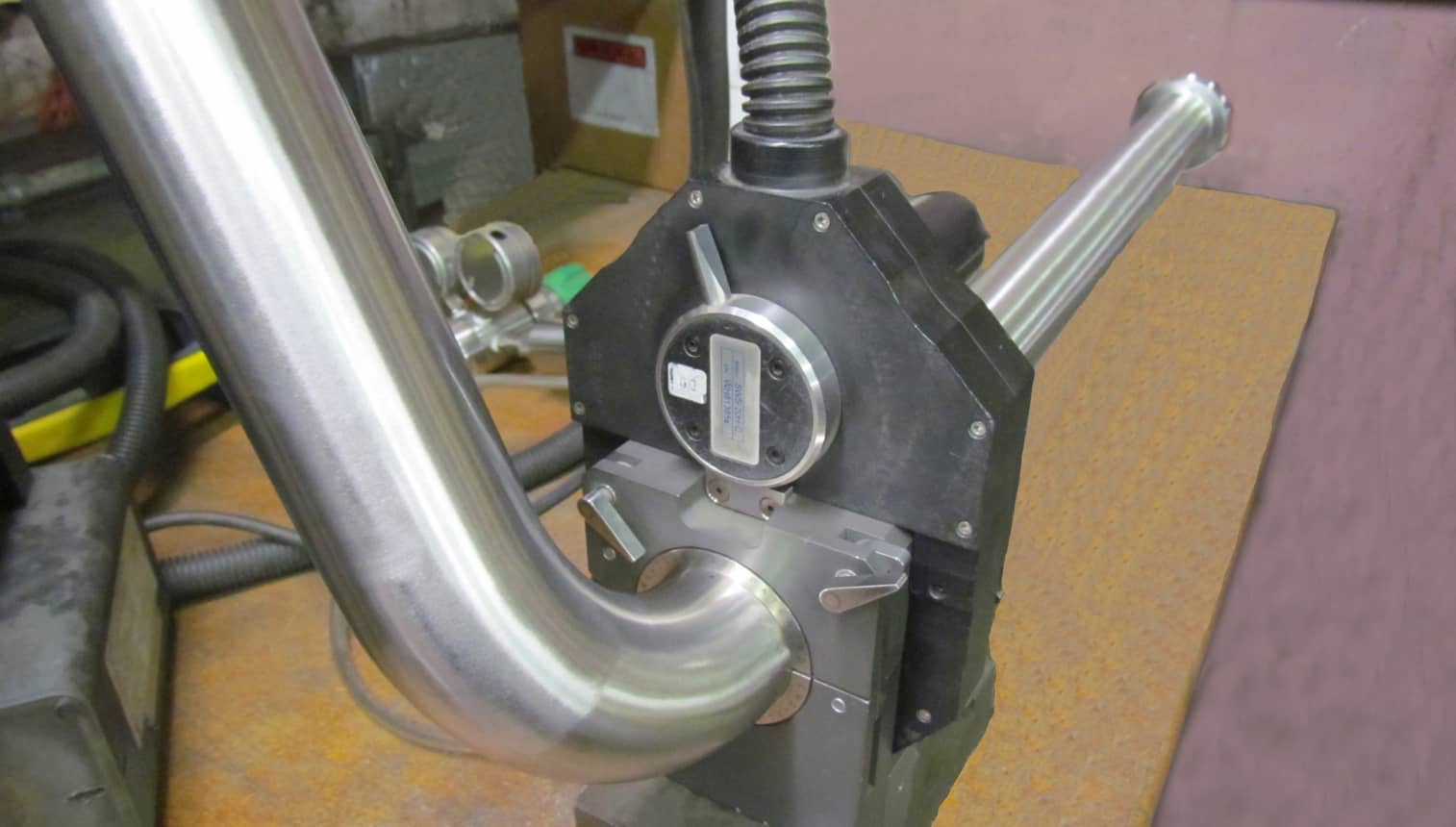
Orbital Welder
BPE vs Sanitary Elbow
Standards & Certification
PE Certification means that a company has been audited and certified by ASME to supply products that meet or exceed the ASME-BPE standard.
The company’s quality system and products manufactured are audited for compliance.
Traceability
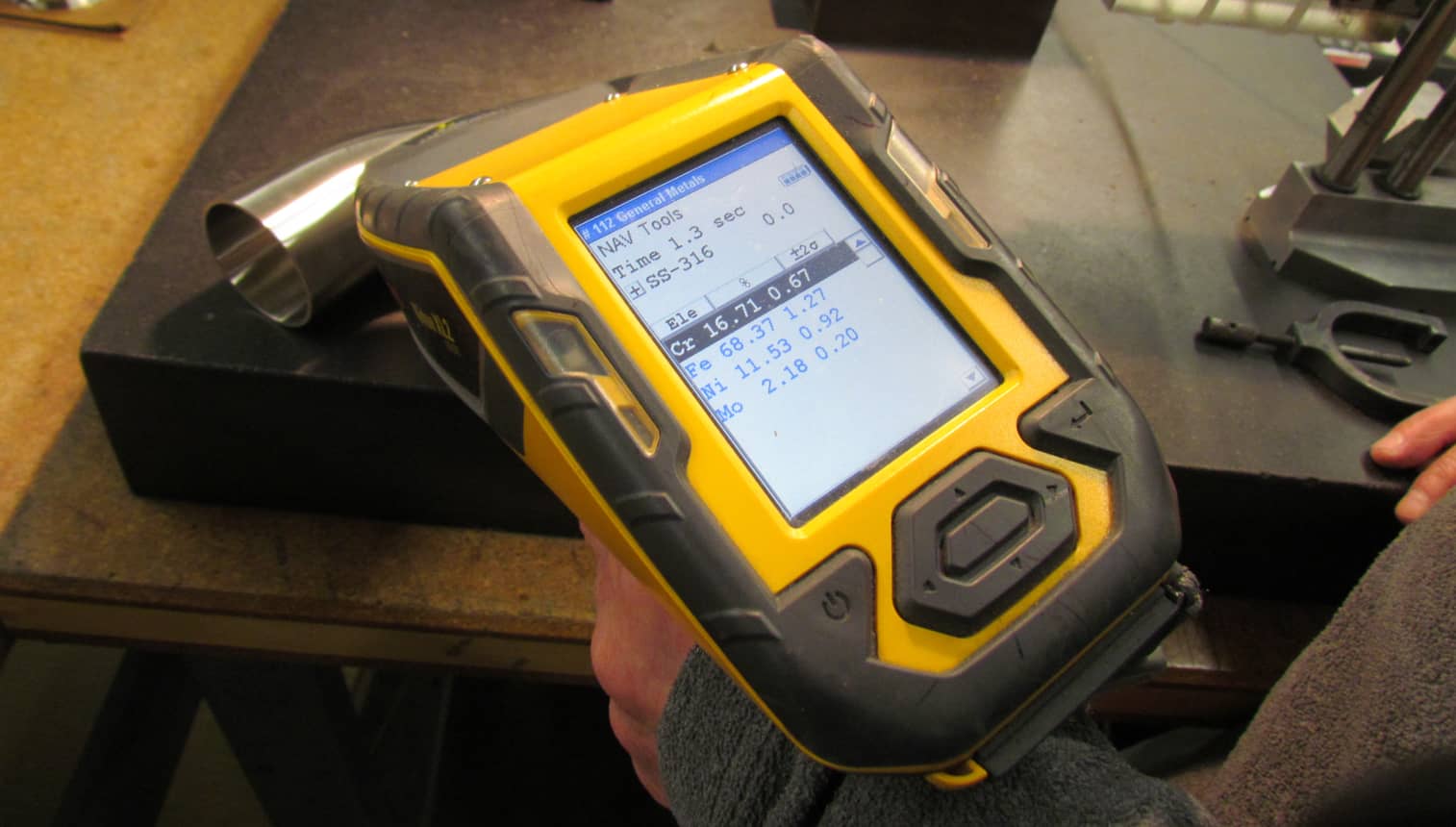
Traceability is critical for BPE fittings given the stringent hygienic requirements of bioprocessing end users like pharmaceutical and life science companies. The chemical make-up of the fitting material is defined in the spec.
If the chemical and mechanical make-up of the material does not meet the spec, the part can be rejected. Heat numbers, which identify the manufacturing lot of the steel and are marked on the outside of the part, must be able to be matched up with the corresponding paperwork (called Material Test Reports) as proof that the fitting meets the specified standards.
Material Test Reports
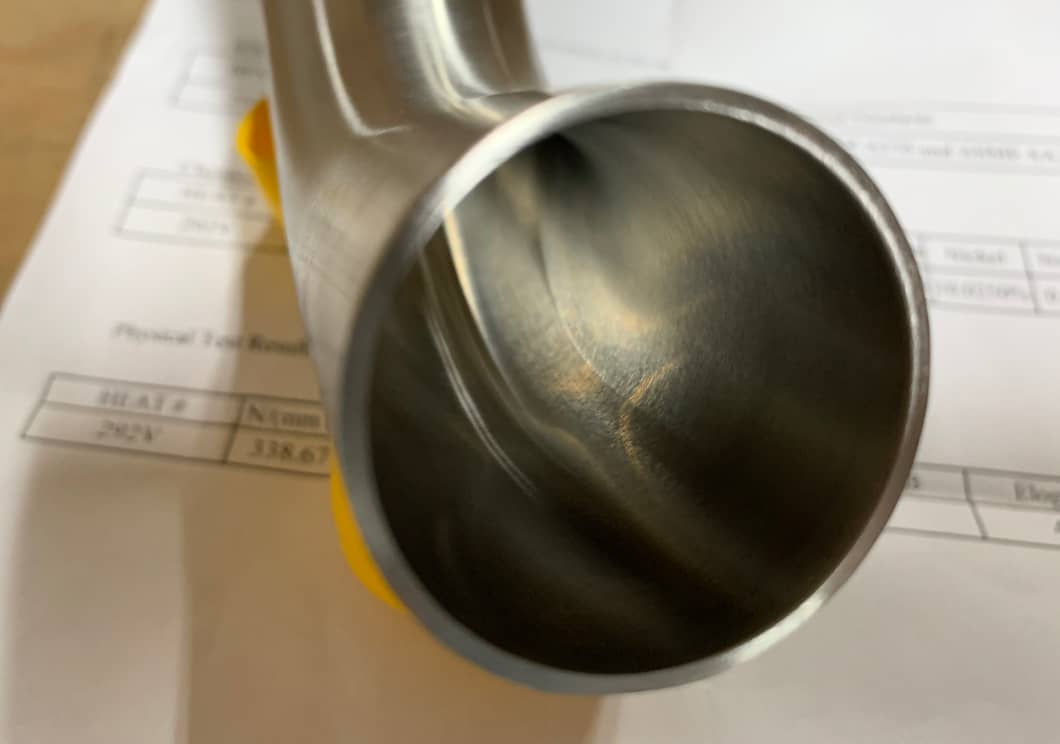
MTR– Material Test Report (or CMTR…C is for Certified) is a document from the mill where the steel is made that states the mechanical and chemical properties of the steel. The MTR document travels with the steel as it is converted into products such as fittings and is used for material traceability and verification.
A part can be rejected if it does not meet the properties defined in the BPE spec. An MTR must be provided with each fitting. The fitting is also marked with a heat number that is assigned at the mill, off the MTR.
BPE Fitting with Heat Number and Material Test Report
Conclusion
BPE fittings are used in the manufacturing of sensitive goods such as medicines and other pharmaceutical products. Given the nature of these products, they are held to a higher level of precision and utilize surface finishes smoother than their standard counterparts.
Documentation and packaging is critical throughout the manufacturing process of BPE so that end-users can trace their products back to inception should anything go wrong throughout production.
With a better understanding of these fittings, you should feel more comfortable in choosing which ones your manufacturing process requires.
If you have any questions, please don’t hesitate to contact us by phone or email. We would be more than happy to further explain any of the above or answer any specific inquiries you have about this important market.
Just one example of the precision equipment businesses like yours must rely on is tri-clamp fittings. By better understanding what they are, how they work, and the options available, you’ll know which ones to choose for your unique manufacturing processes.

Take a look through our inventory and we’re confident you’ll find what you need.
If you do have any questions, please don’t hesitate to contact us phone email. We would be more than happy to further explain any of the above or answer any specific inquiries you have about this important component.